
| 
|

 Malverns Worldwide - Malvern Hill, Virginia
Malverns Worldwide - Malvern Hill, VirginiaTHE BATTLE OF MALVERN HILL
also known as the Battle of Poindexter's Farm
Malvern Hill
Virginia
United States of America

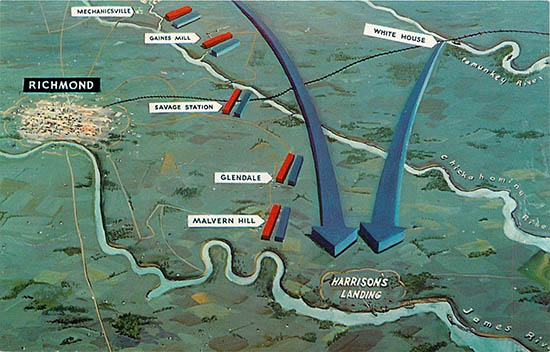
The hill itself is a modest elevation just over 2 miles north of the James River. Its strength lay not in its height, but rather in its fields of fire. Gently sloping open fields lay in front of the Union position, forcing any Confederate attacks against the hill to travel across that barren ground. McClellan unlimbered as much artillery as he could at the crest of the hill, facing in three directions. Nearly 70,000 infantry lay in support, most of them crowded in reserve on the back side of the hill.

The dominance of the position enabled less than one-third of the Union army to defeat a larger chunk of the Confederate army. Confederate leaders and soldiers alike could look back on poor command and control as the principal cause of their defeat. The casualty totals were more balanced than expected for a battle in which the outcome never was in doubt. Slightly more than 5000 Confederates fell killed and wounded, while roughly 3000 Union soldiers met a similar fate.


Website: Click Here
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
1) TOPOGRAPHICAL LOCATION:
United States of America Malverns Worldwide
Malverns Worldwide2) LANDSCAPE:
FarmlandRolling Countryside
3) INFORMATION CATEGORY:
Springs and Wells General InterestHistory & Heritage
4) MALVERN SPRING OR WELL SITE DETAILS:
General Sightseeing Location5) GENERAL VISITOR INFORMATION:
Access By RoadAccess On Foot
Free Public Access
Free Parking Nearby
Disabled access
Accessible All Year



